March 9, 1970

https://www.occ.treas.gov/about/who-we-are/history/previous-comptrollers/bio-22-william-camp.html
March 10, 1970
Congress creates the National Credit Union Administration as an independent agency to charter and supervise federal credit unions. The National Credit Union Share Insurance Fund is also formed, insuring share deposits at federally insured credit unions up to $20,000, the same level as FDIC insurance. Until this point, credit unions had operated without federal deposit insurance.
April 1, 1970

1970
There are approximately 13,800 FDIC-insured institutions with estimated insured deposits of about $350 billion.
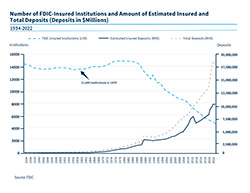
Chart of the number of FDIC-Insured institutions and amount of estimated insured and total deposits - 1970
The FDIC's first use of open-bank assistance occurs with Unity Bank and Trust Company a $9.3 million bank in Boston, Massachusetts. In July, the FDIC Board approved a loan of $1.5 million to the bank, which had been established in 1978 as a community venture to serve the minority community of Roxbury-Dorchester in Boston. The decision to use open-bank assistance was made because the FDIC Board deemed the institution essential to providing adequate banking service to the community, as required by the statutory authority provided to the FDIC in 1950.
December 22, 1971
The Hunt Commission Report is published with recommendations for changes in the regulation of the U.S. financial system. Appointed by President Richard M. Nixon, the Commission proposed, among other changes, eliminating deposit rate ceilings and authorizing a wider range of powers for financial institutions.
National Automated Clearing House (ACH) is set up to modernize the payments system.
https://www.nacha.org/content/history-nacha-and-ach-network
October 8, 1974
Franklin National Bank fails, at the time the largest bank failure in the FDIC's history. The FDIC attributed the bank's failure to losses resulting partly from large foreign exchange trading losses. At the time of its closure, the bank had assets of about $3.6 billion. European-American Bank and Trust Company assumed substantially all of Franklin's $1.4 billion in deposit liabilities for a purchase price of $125 million. Another bank acquires Franklin's trust business.
October 28, 1974
Deposit insurance coverage increases to $40,000 under a law signed by President Gerald R. Ford.
With significant inflation and a rise in interest rates to combat it, open-market instruments again have a yield much higher than savings and loans pay, and funds again moved out of thrifts. With this as a background, Congress again debates raising the deposit insurance ceiling. Both the FDIC and Federal Home Loan Bank Board support an increase, noting it would generate only a marginal increase in risk to the deposit insurance funds.

Image of FDIC $40,000 Deposit Insurance Limit Sign
For the increase in deposit insurance coverage, see Christine M. Bradley, “A Historical Perspective on Deposit Insurance Coverage,” FDIC Banking Review 13 no.2 (2000): 1-25, https://www.fdic.gov/analysis/archived-research/banking-review/br2000v13n2.pdf
February 1975
The Basel Committee on Banking Supervision holds its first meeting following its creation in 1974. The committee is intended to improve financial stability by increasing the quality of banking supervision internationally and by creating a mechanism to coordinate banking supervision among its members.
https://www.bis.org/bcbs/history.htm
December 31, 1975
The Home Mortgage Disclosure Act of 1975 is signed into law by President Gerald R. Ford. The law requires certain depository institutions to disclose mortgage lending information and to make such information available to the public. The FDIC has the power to enforce the act for state nonmember banks it examines and for certain non-federally insured institutions.
March 16, 1976

https://www.occ.treas.gov/about/who-we-are/history/previous-comptrollers/bio-23-james-smith.html
March 18, 1976

June 1, 1977

October 12, 1977
The Community Reinvestment Act of 1977 is signed into law by President Jimmy Carter.
The law requires each bank regulatory agency to assess how banks meet the lending needs of low- and moderate-income communities within their geographic markets and to do so in a safe-and-sound manner. Historically, banks had refused to lend or offer financial products in these neighborhoods.
https://www.federalreservehistory.org/essays/community-reinvestment-act
August 16, 1978

https://www.occ.treas.gov/about/who-we-are/history/previous-comptrollers/bio-24-john-heimann.html
September 17, 1978
The International Banking Act of 1978 is signed into law by President Jimmy Carter. Among its provisions, this law requires that branches of foreign banks engaged in retail deposit taking in the United States have FDIC insurance.
See, FDIC Annual Report, 1978, 113, https://www.fdic.gov/about/financial-reports/reports/archives/fdic-ar-1978.pdf .
November 10, 1978
The Financial Institutions Regulatory and Interest Rate Control Act of 1978 is signed into law by President Jimmy Carter.
This law:
- Expands the enforcement powers of the financial regulatory agencies by authorizing them to issue cease-and-desist orders against directors and officers and to impose civil money penalties for violations of law or of final cease-and-desist orders.
- Permits regulators to remove directors and officers who threaten an institution's soundness.
- Imposes certain restrictions on lending to bank insiders.
- Gives financial regulators the power to disapprove changes in control of financial institutions.
- Gives the FDIC authority over the establishment and operation of foreign branches and the acquisition of the shares of foreign banks by insured state nonmember banks.
- Raises the deposit insurance coverage limit on individual retirement accounts (IRAs) and Keogh accounts (Keogh plans are tax-deferred pension plans available to self-employed individuals or unincorporated businesses) from $40,000 to $100,000.
See FDIC Annual Report, 1978, 113. https://www.fdic.gov/about/financial-reports/reports/archives/fdic-ar-1978.pdf .
February 7, 1979

March 10, 1979
The Federal Financial Institutions Examination Council (FFIEC) is established. In addition to the FDIC, its members are the Federal Reserve Board of Governors, the National Credit Union Administration (NCUA), and the OCC. (The Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB) would be added to its members upon the CFPB's creation in 2010).
