There are approximately 13,500 FDIC-insured institutions with estimated insured deposits of approximately $26.6 billion.
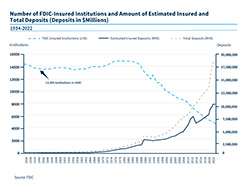
Chart of the number of FDIC-insured institutions and amount of estimated insured and total deposits - 1940
The FDIC moves half of its 500 Washington, DC, employees to Chicago for the duration of World War II in response to President Roosevelt's request that civilian agencies make office space available in Washington.

Image of an FDIC World War 2 Poster
April 27, 1942
FDR's Executive Order No. 9148 temporarily makes the FDIC the regulator of about 4,000 federal credit unions, allowing the Farm Credit Administration, which had supervised them, to concentrate on its core responsibilities during the war. In 1945, Congress made this decision permanent. But the FDIC believed that continuing as credit union regulator would detract from its main responsibilities of bank supervision and deposit insurance and that the public might erroneously believe that the FDIC insured credit union deposits, which were not covered by federal deposit insurance (that did not occur until 1970). Congress moved credit union regulation to the Federal Security Agency in 1948.
October 15, 1945

https://www.occ.treas.gov/about/who-we-are/history/previous-comptrollers/bio-19-preston-delano.html
The insurance fund reaches $1 billion.
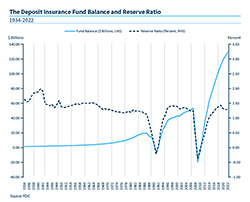
FDIC Deposit Insurance Fund Baland and Reserve Ratio
January 5, 1946

The FDIC repays to the U.S. Treasury the initial capital ($289 million) provided by the U.S. Treasury and the Federal Reserve banks in 1934.

Photo of FDIC Chairman Maple Harl (right) presenting check for $146 million to Undersecretary of the Treasury Wiggins in 1947.
